Robotics deals with the design, construction, operation, and use of robots, as well as computer systems for their control, sensory feedback, and information processing. These technologies are used to develop machines that can substitute for humans and replicate human actions. It's thus an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and science that includes mechanical engineering, electronic engineering, information engineering, computer science, and others.
Robots have been gaining traction over the past few years and they are now been generally accepted as the new kids who are leading the next industrial revolution.
People often confuse Robotics and artificial intelligence. So, whats the difference? Is robotics part of AI? Is AI part of robotics?
What is the difference between the two terms? We answer this fundamental question.
Robotics and artificial intelligence serve very different purposes. However, people often get them mixed up. A lot of people wonder if robotics is a subset of artificial intelligence or if they are the same thing. We will discuss machine learning in our next article.
Are Robotics and Artificial Intelligence the Same Thing?
The first thing to clarify is that robotics and artificial intelligence are not the same thing at all. In fact, the two fields are almost entirely separate.
A Venn diagram of the two would look like this:
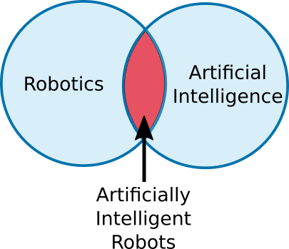
I guess that people sometimes confuse the two because of the overlap between them: Artificially Intelligent Robots.
To understand how these three terms relate to each other, let's look at each of them individually.
What Is Robotics?
Robotics is a branch of technology which deals with robots. Robots are programmable machines which are usually able to carry out a series of actions autonomously, or semi-autonomously.
In my opinion, there are three important factors which constitute a robot:
- Robots interact with the physical world via sensors and actuators.
- Robots are programmable.
- Robots are usually autonomous or semi-autonomous.
I say that robots are "usually" autonomous because some robots aren't. Telerobots, for example, are entirely controlled by a human operator but telerobotics is still classed as a branch of robotics. This is one example where the definition of robotics is not very clear.
It is surprisingly difficult to get experts to agree exactly what constitutes a "robot." Some people say that a robot must be able to "think" and make decisions. However, there is no standard definition of "robot thinking." Requiring a robot to "think" suggests that it has some level of artificial intelligence.
However you choose to define a robot, robotics involves designing, building and programming physical robots. Only a small part of it involves artificial intelligence.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science. It involves developing computer programs to complete tasks which would otherwise require human intelligence. AI algorithms can tackle learning, perception, problem-solving, language-understanding and/or logical reasoning.
AI is used in many ways within the modern world. For example, AI algorithms are used in Google searches, Amazon's recommendation engine and SatNav route finders. Most AI programs are not used to control robots.
Even when AI is used to control robots, the AI algorithms are only part of the larger robotic system, which also includes sensors, actuators and non-AI programming.
Often — but not always — AI involves some level of machine learning, where an algorithm is "trained" to respond to a particular input in a certain way by using known inputs and outputs.
The key aspect that differentiates AI from more conventional programming is the word "intelligence." Non-AI programs simply carry out a defined sequence of instructions. AI programs mimic some level of human intelligence.
What Are Artificially Intelligent Robots?
Artificially intelligent robots are the bridge between robotics and AI. These are robots which are controlled by AI programs.
Many robots are not artificially intelligent. Up until quite recently, all industrial robots could only be programmed to carry out a repetitive series of movements. As we have discussed, repetitive movements do not require artificial intelligence.
Non-intelligent robots are quite limited in their functionality. AI algorithms are often necessary to allow the robot to perform more complex tasks.
Therefore,robotics and artificial intelligence are really two separate things. Robotics involves building robots whereas AI involves programming intelligence.


